
In addition, they are not "contaminated" by being grown with other cells. Bush sufficient? Hundreds of stem cell lines have been created since 2001, and they are much more flexible and easier to work with than the lines formed almost a decade ago. Why do UNMC scientists need to use embryonic stem cell lines created after 2001? Aren't the lines funded under President George W. It is this combined knowledge that will ultimately generate safe and effective therapies.Ĥ. All are part of a research effort that seeks to expand our knowledge of how cells function, what fails in the disease process, and how the first stages of human development occur. Research on human embryonic stem cells, somatic cell nuclear transfer and ‘adult’ or tissue-specific stem cells needs to continue in parallel. Researchers need to determine whether the reprogrammed cells really can give rise to specialized cells that are indistinguishable from the specialized cells formed by embryonic stem cells.
Uses of adult stem cells skin#
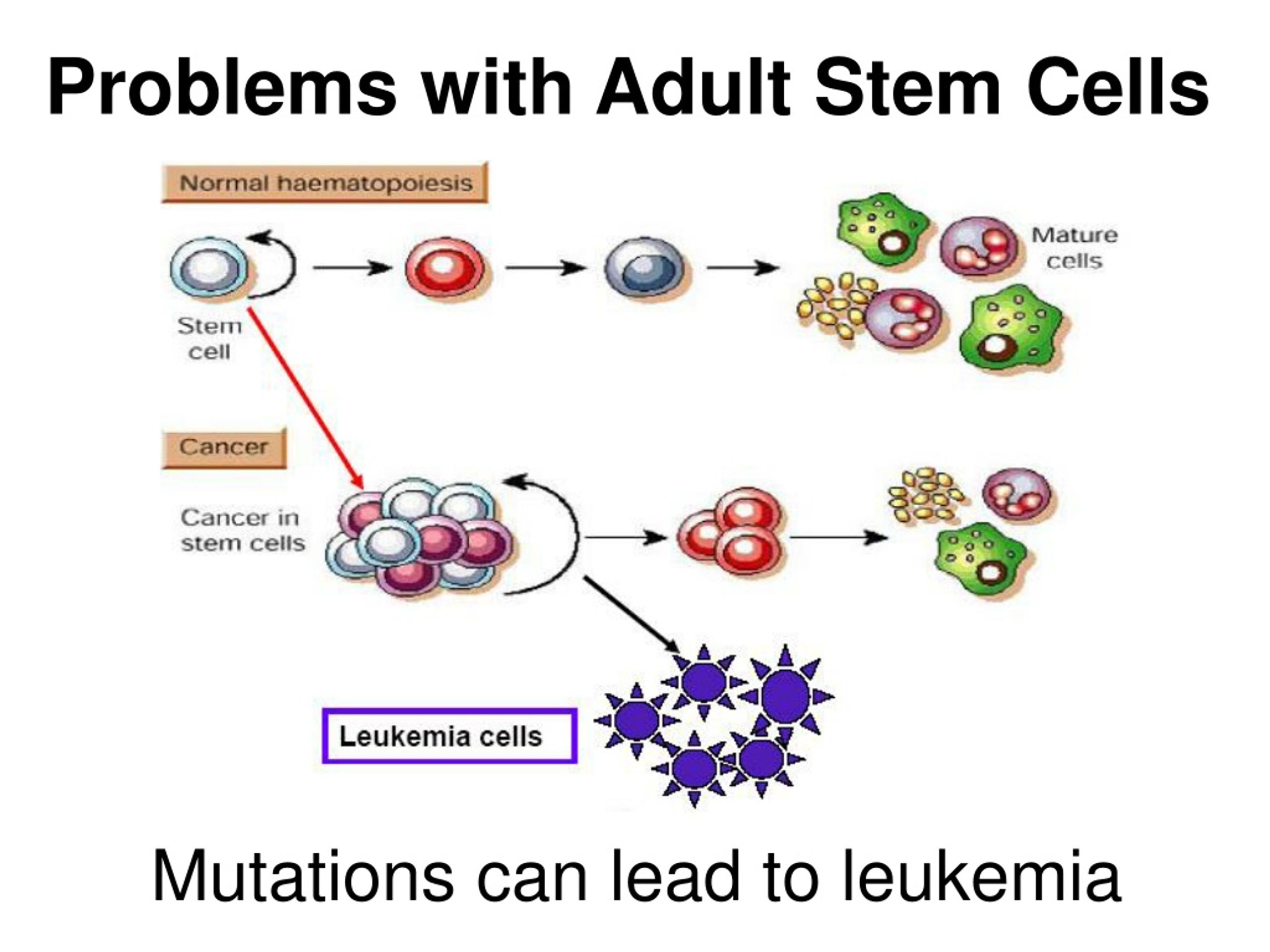
The standard technique to create iPS cells uses viruses to transfer the reprogramming genes into the skin cells. Why do researchers need embryonic stem cells now that they can reprogram adult skin cells to create induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPS cells, which mimic embryonic stem cells? Opponents of embryonic stem cell research prefer iPS, but researchers still need access to embryonic stem cells because the study of iPS cells is in its infancy, and the reprogramming approach may have serious limitations. Bone marrow transplantation (transfers blood stem cells) is a well-established treatment for blood cancers and other blood disorders.ģ. In addition, retinal regeneration with stem cells isolated from the eyes can lead to a possible cure for damaged or diseased eyes and may one day help reverse blindness. In theory, any condition in which there is tissue degeneration can be a potential candidate for stem cell therapies, including Parkinson's disease, spinal cord injury, stroke, burns, heart disease, Type 1 diabetes, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, muscular dystrophy and liver diseases. Currently, researchers are investigating the use of adult, fetal and embryonic stem cells as a resource for various, specialized cell types, such as nerve cells, muscle cells, blood cells and skin cells that can be used to treat various diseases. Replacing diseased cells with healthy cells, a process called cell therapy, is a promising use of stem cells in the treatment of disease this is similar to organ transplantation only the treatment consists of transplanting cells instead of organs.
The development of a range of human tissue-specific and embryonic stem cell lines will provide researchers with the tools to model disease, test drugs and develop increasingly effective therapies. This is knowledge that is required to work out what goes wrong during disease and injury and ultimately how these conditions might be treated. Stem cell research contributes to a fundamental understanding of how organisms develop and grow, and how tissues are maintained throughout adult life. What are the potential uses of human stem cells?

Learn more at UNMC's Regenerative Medicine Project.Ģ. For example, by administering stem cells, or specific cells that are derived from stem cells in the laboratory or by administering drugs that coax stem cells that are already present in tissues to more efficiently repair the involved tissue. Stem cells are frequently used in regenerative medicine research and therapies in several ways. The term regenerative medicine is often used to describe medical treatments and research that restore the function of organs or tissues. What is regenerative medicine? The goal of regenerative medicine is to repair organs or tissues that are damaged by disease, aging or trauma, such that function is restored, or at least improved.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
